Today's newsletter has a preharvest focus. The Orchard Outlook Committee has resumed meeting for the next few weeks to offer preharvest recommendations. Note that although heat accumulated so far this season is on average, degree days may be misleading for harvest estimates because heat observed after flowering was above-average. Late season fungicides and apple maggot insecticides are sorted from longest to shortest preharvest interval for easy reference. The wet and warm year is encouraging lush growth that competes for calcium nutrition so calcium applications are highly recommended. Strategies for harvest fruit quality are discussed.
Table of Contents:
- 2023 Degree Day Accumulations
- Precipitation
- Reminders about Fungicide Preharvest Intervals (PHI)
- Apple Storage/Pinpoint Scab
- Apple - Black Rot
- Apple - Flyspeck and Sooty Blotch
- Preharvest Management of Apple Storage Rots and Fungi
- Fire Blight Management
- White apple leafhopper
- Potato leafhopper
- Apple maggot
- Leaf Tissue Sampling for Nutrient Analysis
- Soil Sampling for Nutrient Analysis
- Calcium Nutrition
- Mowing and Weed Control
- Nursery Budwood Sanitation
- Summer Pruning for Red Colour
- Ethrel cannot be applied to bearing fruit trees
- Delaying or Synchronizing Maturity with ReTain and Harvista
- Estimating Bin Requirements
- Reducing Bruising
- Considering Watercore
- Avoiding Internal Browning
- Consequences of Harvesting too Early
- That's a wrap for summer tours!
Although temperatures are average for the entire season, committee members wonder if degree days may be misleading this year if used for estimating a harvest time. The above-average heat accumulated after flowering may contribute to earlier harvest periods so we recommend considering this possibility as you begin to monitor for maturity.
Figure 1: Heating degree day accumulations for plant (above 5°C) and insect (above 10°C) development from March 1 to August 7 for the past 17 seasons. Provided by Jeff Franklin (AAFC).
- Approximately 1% less plant development heat units compared to the 5-year average, and equal to the 10-year average.
- Approximately 6% less plant development heat units compared to 2021, and 4% less compared with 2020.
- Approximately equal insect development heat units compared to the 5-year average, and 1% more compared to the 10-year average.
Precipitation
Precipitation this season was below-average in April and May and above-average in June and July. Table 1 data is from Kentville and provided by Jeff Franklin (AAFC).Table 1: Precipitation recorded in Kentville for the 2023 season compared with the 25-year mean. Provided by Jeff Franklin (AAFC).
Late Season Diseases
Reminders about Fungicide Preharvest Intervals (PHI)
Table 2: Fungicide products for control of summer diseases listed from longest preharvest interval to shortest preharvest interval. Includes notes about diseases controlled and re-entry intervals (REIs).
Apple Storage/Pinpoint Scab
Pinpoint scab results from infections that occur late in the growing season. Small black dots appear as infections on the skin of the apple. In some cases, the fruit infections do not appear until after the fruit has been placed in storage, however, the infections do occur prior to harvest.Recommendations:
- Fungicide protection maintained through to early September can help to prevent these late season scab infections and provide some protection against storage rots. Note the risk of summer diseases if spray programs are stretched to the limit. Once the 10-day interval has been reached, it is better to re-apply fungicide protection prior to rainfall or possible infection rather than after. In a warm and wet season such as this, the risk of diseases is high.
- Late season fungicide treatment is highly recommended in blocks that have leaf and/or fruit scab. Scab lesions that appear to be inactive at this time of the year can become active again in the fall under cool wet weather conditions.
- Pay special attention to the tops of tall trees that might not have had adequate fungicide coverage. Ambrosia trees in particular are very susceptible to scab and the fruit are stored for a long period of time.
- Folpet (Folpan/Follow) is considered a cousin to Captan and is similarly a hot product that has the potential to cause fruit russetting. Do not use Folpan close to oil sprays or products containing surfactants. Also, be wary of tank mixes with liquid nutrients that are formulated to maximize uptake.
Apple – Black Rot
The black rot fungus infects fruit during warm rains from petal fall to harvest. Captan is an effective protectant for high density orchards that have a history of black rot. However, consider Captan where practical in terms of label restrictions for re-entry intervals. Folpan has a relatively shorter REI for hand thinning. Merivon has activity but group 7 + 11 products should not be used more than 4 times each year. Fungicides would need to be applied prior to the wetting event.Apple - Flyspeck and Sooty Blotch
These summer diseases develop on the surface of the fruit in midsummer until harvest. They are caused by fungi that overwinter in dead twigs and the fungi tend to cause more infections under conditions of moderate temperature, high humidity and rainfall.Preharvest Management of Apple Storage Rots and Fungi
A well-timed preharvest chemical control can go a long way to prevent storage rots. Black rot, flyspeck, sooty blotch and brooks spot are preharvest issues that infect fruit in the orchard. Fungal spores that land on unprotected fruit can germinate and show up as infections in storage. Fruit with bruises and punctures are even more susceptible to rot, especially when fruit are harvested during a wet period. Blue and gray moulds can invade only damaged fruit. Sooty blotch won’t cause decay but it does shorten fruit storage life by increasing water loss.Recommendations:
- The group 7 & 11 products Pristine and Merivon can be applied up to 5 days before harvest. They are labelled for the control of scab, black rot, flyspeck, and sooty blotch. The short PHI and good activity are especially helpful for protecting apples being placed in long-term storage.
- Monitor precipitation during harvest, especially for late-season varieties. Cumulative rainfall of 25-50 mm washes off fungicide protection. The risk of fungicides being washed off is minimized if applied as close to harvest as possible.
- Of course, avoid bruising or wounding to prevent infections of blue and gray moulds. Take the time to educate staff on the proper way to handle fruit.
Fire Blight Management
Fire blight disease is very prevalent this year. Whether it is because late bloom sprays were not applied, there were carryover infections from last year, it was too wet for timely management, or hail damage was unnoticed.
Recommendations:
- Monitor nursery trees and young trees to remove trees with infections. Deer are spreading infections where they graze on young tissue.
- Do not break off branches with fire blight infections as you navigate the orchard. Research shows that the bacteria becomes systemic in the tree because branches are not adequately removed. There are then a high number of new infections and significantly more canker tissue and cankers on structural wood.
- Prune out fire blight infections on young trees in the current year, don't wait for winter. Trees 8 years old and younger are at the greatest risk of rootstock blight.
- Remove fire blight strikes at least 2-4 ft below active infections to remove the leading edge of the bacteria. The younger the tree, the deeper the cut. Being aggressive at the first sign of symptoms will help prevent the re-occurrence of symptoms and the need for continuous cutting back. Repeat tree inspections.
- Cut out infections when a period of 2 dry days are in the forecast. Leave prunings in orchard laneways to let dry thoroughly for several weeks. If cutting a whole tree consider letting it dry while attached to the trellis. Don’t make piles that will prevent the wood from drying.
Insects
Insect management programs should be based on grower monitoring and/or scouting reports.
- White apple leafhopper
- Nymphs from the second generation appear and cause feeding damage in early August. Insecticides labelled for leafhoppers include Assail/Aceta, Calypso/Theme, Savanto Prime and Exirel.
- Potato leafhopper
- The potato leafhopper feeds on the young leaves of terminal shoots leading to yellowing at leaf edges, and cupping that will eventually turn brown. Adults are pale yellow-green and walk sideways whereas the white apple leafhopper is white and moves forward and back.
- Potato leafhoppers can transmit fire blight. Their presence in young plantings and nurseries is concerning, especially in areas of active fire blight infections.
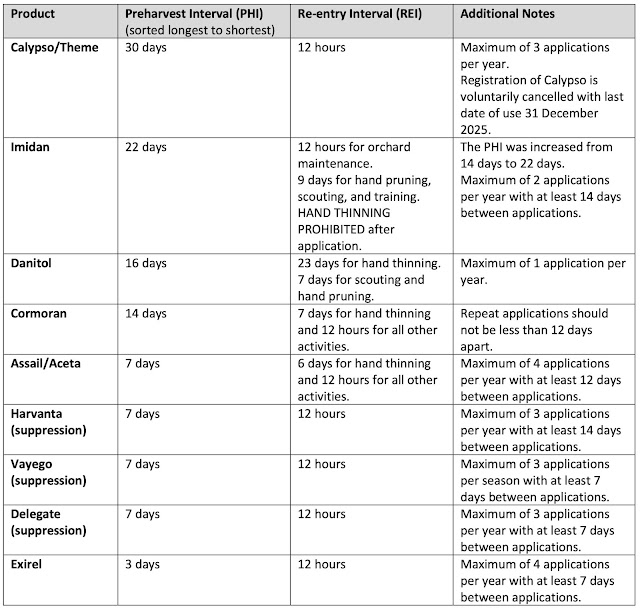
- Apple Maggot
- Table 3 provides a list of insecticide products for apple maggot control with their respective preharvest and re-entry intervals.
- The apple maggot inspection program began this week.
- Maggot catches are high at this time of year and egg laying will continue into September. Flies emerge over a period of time so for satisfactory maggot control, monitor the presence of apple maggot flies to inform treatment programs. Remember, a single female can lay hundreds of eggs so do not stop treatment prematurely.
- Clean maggot traps 7 to 10 days after treating a block for maggot and monitor for new trap captures. Re-treat if new maggot flies are caught.
- Significant rainfall will wash off insecticide residues that are needed to ward off apple maggot flies. Re-treatment is required after 10-14 days or cumulative rainfall of 12.5-25 mm (0.5-1 inch). Danitol and products registered for suppression are expected to have a relatively shorter field residual life of 7-10 days.
- Apple maggot flies are weak flyers so a border/perimeter spray of Imidan near known hotspots may be an approach to help kill adult flies from the source. (Being cognizant of PHI and REI).
- Apple maggots pupate in the soil and may not emerge until up to four years later. Therefore, several years of diligent management are required to reduce the resident insect population.
Table 3: Insecticide products for control of apple maggot listed from longest preharvest interval to shortest preharvest interval. Includes re-entry intervals (REIs) and additional information.
Figure 2: An apple maggot larva feeding on Honeycrisp. A single female fly can lay hundreds of eggs so do not stop treatment prematurely.
Horticulture
Leaf Tissue Sampling for Nutrient Analysis
Nutrient levels in leaf tissues change throughout the growing season. The nutrient analysis for apple tree leaves has historically been done after terminal buds set and recommendations are based on that specific timing (late July to early August in Nova Scotia). Collecting samples prior to or after the specified period may give inaccurate nutrient level readings. Annual fertilizer applications should be based on tissue analysis reports and other factors such as pruning, vegetative growth and anticipated crop load.
Recommendations:
Collect leaves for nutrient analysis after terminal buds set on this season’s extension growth. Complete sampling by about mid-August.
The protocol:
- A sample usually represents a block of orchard 1 to 2 hectares in size.
- Sample 10 apple leaves from each of 10 representative trees of the same variety for a total sample size of 100 leaves. Sample from the same trees every year to limit the variation between years. Try marking the tree with spray paint.
- Collect leaves from the mid-point of the current year’s growth from all sides of the tree.
- Place the leaf samples in a paper bag.
- If there are problem areas within the orchard, then sample trees in the areas separately.
- The leaf sample needs to be submitted as soon as possible after collection in order to obtain an accurate nutrient analysis. If the sample cannot be submitted right away, refrigerate until it can be submitted.
- Always label samples with the grower or farm name, mailing address, phone number, farm registration number, orchard block name, variety and sample number.
- Take an accurate sample by reviewing some guidelines on 'How to take a plant tissue test'
Soil Sampling for Nutrient Analysis
A leaf nutrient test tells you whether a nutrient has been absorbed. A soil analysis, on the other hand, shows what levels are available. If a tree cannot uptake nutrients from adequate soil levels then perhaps your limiting factor is not related to nutrient availability and is more likely related to compaction, nematodes or pathogens affecting the root system. Or more simply, a soil nutrient test could determine a soil nutrient deficiency.
Recommendations:
- Soil samples do not need to be collected on an annual basis but should be collected at least once every three years.
- Two to four soil cores should be taken at the drip line from each of 10 trees. The soil cores should be mixed and a representative sample placed in a soil box or sealable plastic bag for analysis.
- Early August is a good time to sample orchard soil unless the soil is unusually dry or recently leached by heavy rains. If the soil is too dry it is very difficult to extract full 0-15 cm (0-6") soil samples and a better sample will be obtained by waiting until light rain has moistened the topsoil.
Calcium Nutrition
- This year the wet weather is encouraging plenty of vegetative growth. The leaves compete with the fruit for calcium so the lush growth may dilute the calcium in fruit. Therefore, calcium applications are highly recommended this year.
- The recommended rate is 4 to 14 pounds of elemental calcium per acre in a season spread over six to eight cover sprays.
- Low rates will not cause leaf burn but will likely lead to only minor control of bitter pit and likely will not enhance storage life of the fruit.
- High rates may lead to some leaf burn, give good control of bitter pit, and may also enhance storage life of the fruit. High rates are recommended for Honeycrisp.
- Calcium applied at two-week intervals is better than occasional, high-rate applications.
- For help calculating the amount of elemental calcium you are applying in each spray, visit Penn State Extension to download a calcium rate calculator. The percentage of elemental calcium will be listed on the label of your product of choice. Check formulated calcium products because they may not contain as much calcium as you expect.
- Ca has very low movement within the tree and needs to be applied directly to the fruit surface to be absorbed. Therefore, thorough coverage is important to cover developing fruit.
- Calcium chloride flake (77% Ca) is the most economical Ca material to use but also the highest risk for foliar burn. Calcium chloride flake is safe when applied at 4.5 kg per 1000 L of spray solution. The risk of leaf or fruit damage from calcium is highest in hot weather. Susceptible varieties can develop lenticel spotting if damaged.
- Calcium chloride flake can be rough on equipment. Use a pressure washer to clean equipment. Consider spraying your spray equipment with superior oil before beginning and the calcium will wash off more easily.
- Calcium chloride is a worthwhile management strategy for bitter pit, even if it has to be applied alone. Waiting for a tank mix partner may mean that ideal application timings are missed.
- Note that nutrient product formulations with calcium may contain boron that would interact poorly with water soluble packaging.
Mowing and Weed Control
- Mowing and herbicide strips help to prevent issues with two-spotted spider mite (John Michael Hardman).
- Maintain good weed control during July and August on young plantings that need to develop vegetative growth. Studies have shown that weed competition during this time can have a significant negative impact on early cropping of young blocks.
Nursery Budwood Sanitation
- Find a source of budwood that does not have a history of fire blight strikes. Trees that have shown signs of fire blight strikes or that are situated near fire blight infections should be eliminated as a source of budwood. Cut budwood fresh every morning if possible.
- Occasionally sanitize all tools used for budwood collection, storage, and budding by washing in detergent and water and disinfecting with sodium hypochlorite bleach. During bud wood collection and budding, frequently spray hand tools with fresh sodium hypochlorite bleach solution.
- The general recommendation is one part bleach to ten parts of water.
- If bleach is too tough on tools, Lysol and Pinesol at one part product to ten parts of water are good alternatives.
- Do NOT use rubbing alcohol because even at 70% to 99% it allows bacteria to survive (California Agriculture 1991).
Harvest Fruit Quality
Summer Pruning for Red Colour
Vigorous shoot growth in orchards could present a fruit shading problem. Summer pruning could be used to expose the fruit to more sunlight to improve fruit colour. Also, summer pruning controls vigour so it could divert more calcium to fruit. The practice might help reduce the risk of bitter pit.Recommendations:
- Summer pruning should involve making the pruning cuts to one- and two-year old wood. Remove vigorous shoots in the entire canopy but especially at the top.
- Leave the weaker side laterals to supply the fruit with carbohydrates. If you over prune you could end up reducing fruit size.
- Avoid leaving short stubs as they will produce two or more shoots next spring.
- Fire blight is very prevalent this year so leave fire blight infected blocks for last so that terminal buds are set. Sanitize tools between blocks and work in dry weather.
Ethrel cannot be applied to bearing fruit trees
The registration of the product Ethrel has changed. Ethrel cannot be applied to bearing fruit trees so it cannot be used for hastening fruit maturity for early markets.Delaying or Synchronizing Maturity with ReTain and Harvista
Highlights
- As even more new plantings come into bearing, consider the advantages of harvest management tools to help slow fruit maturity as you manage labour resources.
- Both ReTain and Harvista can help reduce the incidence of watercore and internal browning by delaying maturity.
- The economic return for these products is expected to be greatest with good crop loads, high-value varieties, and good fruit quality.
- Consider testing ReTain or Harvista on a small block and talk to others who have experience using them.
ReTain
ReTain’s active ingredient (aviglycine hydrochloride) inhibits the production of ethylene in plant tissues, delaying fruit maturity. Potential benefits of ReTain include harvest management to delay the maturity in blocks of a single variety, improved fruit size (as fruit hangs longer on the tree), maintenance of firmness, and reduced greasiness and cracking. ReTain can also offer additional benefits including improved storage quality. However, Retain can also slow red colour development. Delays to fruit colour development can be minimized by lowering the rate of application or by delaying the harvest period.Recommendations:
- Note that the amount of ethylene produced differs by apple variety and so the variety’s response to ReTain will also differ. McIntosh is a high ethylene-producing variety and the full rate is often needed 3 weeks before harvest to slow its maturity. Sensitive varieties like Gala, Jonagold and Honeycrisp produce low ethylene and are more sensitive and thus greatly delayed by full rates of ReTain.
- ReTain applied 3-4 weeks before harvest will delay the harvest period up to 7 to 10 days.
- The effectiveness of ReTain is dose-dependent and time-dependent. Later applications and smaller doses have less effect on maturity and colour development.
- For a multi-pick harvest, ReTain applied 7 to 14 days prior to the anticipated start of the 1st harvest can improve the quality and storage potential of 2nd and later picked apples. First picks will not be affected but later picks will be delayed. Note the PHI of 7 days.
- Xiameter surfactant is recommended at a concentration of 0.05 to 0.1% (v/v) in the spray tank. To prevent possible spotting on fruit, use the 0.05% (v/v) concentration.
- ReTain is not a systemic product. Good coverage of both fruit and leaves is important to response.
- On the label, there is a caution stating that the fruit on heat- and water-stressed trees may not respond to the product.
Harvista
Harvista (1-methylcyclopropene) is another product for preharvest management. The mode of action is different from Retain because Harvista blocks ethylene action in fruit, even after ethylene has been produced by fruit. Therefore, Harvista can act quickly to slow maturity whereas ReTain requires a timely application to fruit before ethylene production escalates.Recommendations:
- Harvista can be applied 3 to 21 days before the anticipated harvest and at a higher rate for fruit that are more advanced in maturity and producing plenty of ethylene.
- Harvista will delay the harvest period up to 7 to 14 days.
- Typically the product will reduce the number of harvest picks because it helps synchronize the maturation rate.
- Lower rates are recommended for biocoloured apple varieties to allow colour development to progress. It can delay red colour development on Gala and Ambrosia so apply after colour has developed at close to 3 days before harvest. It also reduces stem splits on Gala.
- A customized sprayer system is required for Harvista applications.
- A calibration video is available on the AgroFresh YouTube page.
- The Harvista Calibration Tool is available on Google Play and the Apple Store.
Estimating Bin Requirements
Large apples fill bins a lot quicker than small apples. If fruit in a block are a relatively uniform size, then a little math can help you estimate bin requirements. The crop volume is determined by the number of trees, number of fruit, and fruit size.
To approximate the number of bins required:
- Calculate the number of apples per acre (# trees per acre x avg # apples per tree)
- Refer to table 4 for the # of apples per 17 bu bin of a selected average count size
- Bins/acre = # of apples per acre / # apples per bin for selected count size
Table 4: Number of apples of a selected count size to fill a 17 bu bin.
Example 1: 125 count size
- 1000 trees per acre x 60 apples/tree = 60,000 apples/acre
- There are 2125 apples per bin of 125 count size.
- Bins/acre = 60,000 apples per acre/2125 apples per bin = 28.2 bins/acre
Example 2: 113 count size
- 1000 trees per acre x 60 apples/tree = 60,000 apples/acre
- There are 1921 apples per bin of 113 count size.
- Bins/acre = 60,000 apples per acre/1921 apples per bin = 31.2 bins
Recommendations:
- Now is a great time to consider your bin inventory, repair bins, and ensure bins are well-washed.
Reducing Bruising
Recommendations:
- Apples picked after significant rain will bruise more easily than if they’re picked when the soil has a lower moisture capacity. This information might be helpful for varieties especially sensitive to bruising.
- Let fruit warm up before harvesting. Apples picked in the cool weather of early morning bruise more easily than those picked in the day’s warmth. Generally, susceptibility to bruising decreases gradually from 0 to 15°C.
- Take the time to educate staff about the proper way to perform harvest activities that reduce bruising. For example, pick the bottom of the tree first, don’t overfill the picking bag, avoid long harnesses that let the bag bump against knees when walking, explain the difference between varieties etc.
- Re-grade orchard roads prior to harvest to lessen bumps that would jostle fruit being transported in bins.
- Have an inspector sample fruit from various positions in the bin two times each week and leave at room temperature for 24 hours to check for signs of bruise development.
- If bins of fruit will sit in the orchard during overnight freezing temperatures, place the bins where they will be shaded from direct morning sun. Direct sun will warm the fruit too quickly and can lead to deep and lasting bruises.
Considering Watercore
Watercore is a fruit disorder closely associated with over-mature apples along with several other factors. It happens most frequently in years with high sunshine and lack of cloudy, rainy days. Also, highly coloured and large fruit are most prone to the disorder. Fruit with the disorder have an appearance of water-soaked flesh because the spaces between the cells become concentrated with sugars instead of air. Small signs of watercore can disappear in storage and add sweetness to fruit. However, more serious watercore can reduce gas exchange in the fruit and lead to internal breakdown.Recommendations:
- Mature fruit are more likely to develop the disorder because as fruit mature the starches are converted to sugars. The sugar solution builds up in the fruit. Blocks that have a history of watercore should be harvested before other blocks.
- Consider products to delay harvest maturity. Both ReTain and Harvista labels state delayed onset and incidence of watercore.
Figure 3: An example of watercore symptoms in Honeycrisp from 2018. Note the areas of water-soaked flesh.
Avoiding Internal Browning
Internal browning is likely related to carbon dioxide injury. The disorder frequently occurs in overmature and large fruit that have high carbon dioxide concentrations. In particular, fruit harvested late in the harvest window are most susceptible because as fruit mature their ability to diffuse internal carbon dioxide concentrations decreases. The internal carbon dioxide builds up and increases the chance of injury. Consider using products that delay harvest maturity.Consequences of Harvesting too Early
While trying to avoid overmature fruit, avoid the other extreme as well – immature fruit. Picking fruit too early has penalties. Fruit continue to grow as they mature so a 1/4 inch increase in size from 2 3/8 to 2 5/8 can translate into a 35% increase in fruit volume. It takes just as long to pick one large (88 count) apple as it does to pick one small apple (160 count). But it will take half as long to make up a bushel of large apples than small. So picking cost and time required are less for larger fruit. Picking too early can also sacrifice fruit colour and reduce pack out. Immature fruit bruises easily and is subject to scald, shriveling in storage, and poor flavour.Events and Notices
That's a wrap for summer tours!
Thank you also to the Nova Scotia Fruit Growers' Association for organizing another successful summer orchard tour. The tour features local growers for their achievements and valuable experiences and is an opportunity to share ideas. Throughout the day we took in research trials, long plantings, pre-plant preparation, and shiny equipment. This year the tour covered the west side of the Valley - including Grafton, Aylesford, and Paradise. We even dodged the rain! Thanks to everyone who was involved, especially for the extra effort in planning multiple tours!
Pest Management Guides 2023
All changes new to 2023 are made in red text directly on the guides. The information on all expected changes was summarized in a blog post on March 7.Decision Tables
- Download the 2023 Petal Fall Insecticide Decision Table
- Download the 2023 Prebloom Insecticide Decision Table
- Download the 2023 Fungicide Decision Table
Guides
- Download the 2023 Pome Fruit Management Guide
- Download the 2023 Organic Apple Management Guide
- Download the 2023 Stone Fruit Management Guide
- Download the 2023 Thinners and Growth Regulators Guide
- Download the 2023 Tree Fruit Weed Management Guide
This Orchard Outlook has been published with the input of the Orchard Outlook Committee including this week's participants: Larry Lutz, Bob Prange, Danny Davison, Kari Brown, Jeff Franklin, Suzanne Blatt, Keith Fuller, and Jill MacDonald.
Perennia Food and Agriculture Corp.
Edited by Michelle Cortens, Tree Fruit Specialist